Main Article Content
Abstract
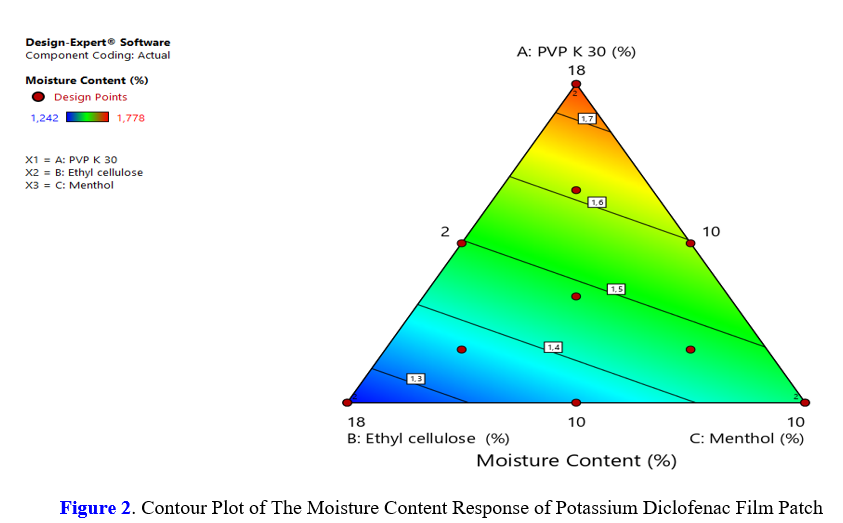
Diclofenac potassium is one of the NSAID drugs which can cause gastrointestinal irritation and damage to the small intestinal mucosa including erosion and ulceration. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of the combination of PVP K 30, ethyl cellulose and menthol on organoleptic, thickness, weight uniformity, moisture and folding resistance of diclofenac potassium transdermal patch.This research is an experimental study that includes an experiment to optimize the formulation of a transdermal patch preparation with the active ingredient potassium diclofenac and a combination of PVP K 30, ethyl cellulose and menthol. The optimization method uses the simplex lattice design method. There are 13 formula designs consisting of a combination of PVP K 30, ethyl cellulose and menthol. Each formula was tested for organoleptic, thickness, weight uniformity, moisture and folding resistance. Then the optimum formula was determined and analyzed using the simplex lattice design method. The combination of PVP K 30, ethyl cellulose and menthol with a simplex lattice design has an effect on the transdermal patch of diclofenac potassium which increases the consistency of the patch surface, reduces the thickness directly proportional to the weight of the patch and increases folding resistance. The proportion of PVP K 30, ethyl cellulose and menthol that can produce the optimum formula for diclofenac potassium transdermal patches with the simplex lattice design on the critical parameters of thickness, moisture, folding resistance and penetration tests, namely PVP K 30 of 14.87%, ethyl cellulose of 10.00% and 5.13% menthol.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
- Arifin, A., Sartini, & Marianti. (2019). Evaluasi Karakteristik Fisik dan Uji Permeasi Pada Formula Patch Aspirin Menggunakan Kombinasi Etil Selulosa dan Polivinil Pirolidon. Jurnal Sains Dan Kesehatan, 2(1), 29–31. https://doi.org/10.25026/jsk.v2i1.103
- Barros, N. R. de, Chagas, P. A. M., Borges, F. A., Gemeinder, J. L. P., Miranda, M. C. R., Garms, B. C., & Herculano, R. D. (2015). Diclofenac Potassium Transdermal Patches Using Natural Rubber Latex Biomembranes as Carrier. Journal of Materials, 2015, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/807948
- Ermawati, D. E., & Prilantari, H. U. (2019). Pengaruh Kombinasi Polimer Hidroksipropilmetilselulosa dan Natrium Karboksimetilselulosa terhadap Sifat Fisik Sediaan Matrix-based Patch Ibuprofen. JPSCR : Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Clinical Research, 4(2), 109. https://doi.org/10.20961/jpscr.v4i2.34525
- Fatmawaty, A., Nisa, M., Irmayani, & Sunarti. (2017). Formulasi Patch Ekstrak Etanol Daun Murbei (Morus Alba L.) dengan Variasi Konsentrasi Polimer Polivinil Pirolidon dan Etil Selulosa. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Sciences, 2(1), 17–20. Available at: https://www.jpms-stifa.com/index.php/jpms/article/view/37
- Fuziyanti, N., Najihudin, A., & Hindun, S. (2022). Pengaruh Kombinasi Polimer PVP : EC dan HPMC : EC Terhadap Sediaan Transdermal Pada Karakteristik Patch yang Baik : Review. Pharmaceutical Journal of Indonesia. 7(2), 147–152. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.pji.2022.007.02.10
- Hermanto, F. J., & Nurviana, V. (2019). Evaluasi Sediaan Patch Daun Handeuleum (Graptophyllum Griff L) Sebagai Penurun PanaS. Jurnal Kesehatan Bakti Tunas Husada: Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Keperawatan, Analis Kesehatan Dan Farmasi, 19(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.36465/jkbth.v19i2.499
- Kumar, S. V., Tarun, P., & Kumar, T. A. (2013). Transdermal drug delivery system for non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs: A review. Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 3(5), 3588–3605. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201815666180605114131
- Matsui, H., Shimokawa, O., Kaneko, T., Nagano, Y., Rai, K., & Hyodo, I. (2011). The pathophysiology of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID)induced mucosal injuries in stomach and small intestine. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 48(2), 154–160. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.10
- Maulina, N. (2021). Pengaruh Pemberian Enhancer Mentol Terhadap Karakteristik Sediaan Natrium Diklofenak Dalam Basis Gel Carbomer-940. Jurnal Sains Farmasi, 2(2), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.36456/farmasis.v2i2.4694
- Mita, S. R., Husni, P., & Setiyowati, D. (2018). In vitro Permeation Study of Ketoprofen Patch with Combination of Ethylcellulose and Polyvynil Pyrrolidone as Matrix Polymers. J Young Pharm, 10(2), 101–105. https://doi.org/10.5530/jyp.2018.2s.20
- Nurmesa, A., Nurhabibah, N., & Najihudin, A. (2019). Formulasi dan Evaluai Stabilitas Fisik Patch Transdermal Alkaloid Nikotin Daun Tembakau (Nicotiana tobacum Linn) Dengan Variasi Polimer dan Asam Oleat. Jurnal Penelitian Farmasi & Herbal, 2(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.36656/jpfh.v2i1.150
- Purnamasari, N., Alatas, F., & Gozali, D. (2019). Formulasi Dan Evaluasi Transdermal Patch Kalium Diklofenak. Kartika: Jurnal Ilmiah Farmasi, 7(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.26874/kjif.v7i1.209
- Puspitasari, K. D., Nurahmanto, D., & Ameliana, L. (2016). Optimasi Hidroksipropil Metilselulosa dan Carbopol terhadap Moisture Content dan Laju Pelepasan Patch Ibuprofen In Vitro. Pustaka Kesehatan, 4(2), 229–234. Available at: https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/JPK/article/view/3033
- Putri, E. D. (2018). Optimasi Perbandingan Konsentrasi Polimer Hidroksilpropil Metilselulosa (HPMC) dan Polimer Etil Selulosa (EC) Pada Matriks Patch Nanoemulsi Hidroklortiazid. Universitas Brawijaya.
- Raissi, S., & Farsani, R.-E. (2009). Statistical Process Optimization Through Multi-Response Surface Methodology. August 2017.
- Setyawan, E. I., Pratama, P. Y. A., & Budiputra, D. K. (2015). Optimasi Formula Matriks Patch Ketoprofen Transdermal Menggunakan Kombinasi Asam Oleat dan Minyak Atsiri Bunga Cempaka Putih (Michelia alba) sebagai Permeation Enhancer. Jurnal Farmasi Udayana, 4(2), 37–44. Available at: https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/jfu/article/view/17110
- Suryani, Musnina, W. O. S., & Anto, A. S. (2015). Optimasi Formula Matriks Patch Transdermal Nanopartikel Teofilin dengan Menggunakan Metode Simplex Lattice Design (SLD). Majalah Farmasi, Sains, Dan Kesehatan, 3(1), 26–32. http://dx.doi.org/10.33772/pharmauho.v3i1.3450