Main Article Content
Abstract
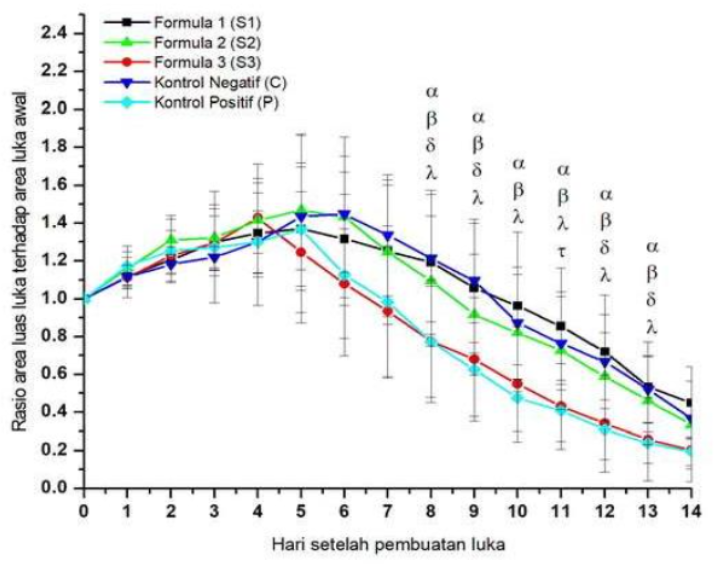
Wounds are referred to as 'Silent Epidemic' because they have a substantial impact if not treated properly. Betel leaf is known to contain compounds that may be used as wound healers. The purpose of this study was to test the spray activity of betel leaf extract (Piper betle L) in healing acute wounds in male Balb/C mice. Spray formula made with various concentrations of betel leaf extract by 3% (S1), 5% (S2) and 7% (S3). The acute wound healing activity test was 15 mice divided into 5 groups S1, S2, S3, P (positive control), and C (negative control). Interventions and observations were carried out for 14 days. The results of observational analysis by calculating the ratio of wound area then One Way ANOVA test and Post Hoc Tukey Cramer test. The results showed that spray of betel leaf extract with a concentration of 7% was not significantly different from P (p>0.05). The conclusion in this study is that sprays of betel leaf extract 3%, 5%, and 7% may be used as an acute wound healer, the best healing activity is shown at a concentration of 7%.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
- Chế Thị, C. H., Nguyễn, H. Đ., & Lê Hoàng, D. M. (2021). Influence of Piper betle L. extract on umbilical cord cells in vitro and potential treating cutaneous wound. Heliyon, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06248
- Demidova-Rice, T., Hamblin, M., & Herman, I. (2013). Acute and Impaired Wound Healing: Pathophysiology and Current Methods for Drug Delivery, Part 1: Normal and Chronic Wounds: Biology, Causes, and Approaches to Care. Adv Skin Wound Care, 25(7), 304–314. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASW.0000416006.55218.d0.Acute
- Dwivedi, V., & Tripathi, S. (2014). Review study on potential activity of Piper betle. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry JPP, 93(34), 9398.
- Ghazali, N. A., Elmy, A., Yuen, L. C., Sani, N. Z., Das, S., Suhaimi, F., Thent, Z. C. (2016). Piper betel leaves induces wound healing activity via proliferation of fibroblasts and reducing 11β hydroxysteriod dehydrogenase-1 expression in diabetic rat. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 7(4), 198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2016.08.008
- Gonzalez, A. C. D. O., Andrade, Z. D. A., Costa, T. F., & Medrado, A. R. A. P. (2016). Wound healing -A literature review. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia, 91(5), 614–620. https://doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164741
- Kartiningtyas, A. T., Prayitno, P., & Lastianny, S. P. (2015). Pengaruh Aplikasi Gel Ekstrak Kulit Citrus Sinensis terhadap Epitelisasi pada Penyembuhan Luka Gingiva Tikus Sprague Dawley. Majalah Kedokteran Gigi Indonesia, 1(1), 86. https://doi.org/10.22146/majkedgiind.9012
- Lawrence, R., P, T., & Jeyakumar, E. (2009). Isolation, Purification and Evaluation of Antibacterial Agents from Aloe Vera. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 906–915.
- Lindholm, C., & Searle, R. (2016). Wound management for the 21st century: combining effectiveness and efficiency. International Wound Journal, doi: 10.11. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12623
- Mahyudin, F., Edward, M., Basuki, M. H., Basrewan, Y., & Rahman, A. (2020). Modern and Classic Wound Dressing Comparison in Wound Healing, Comfort and Cost. Jurnal Ners, 15(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.20473/jn.v15i1.16597
- Mandal, U. K., Chatterjee, B., Husna, F., & Pauzi, B. (2016). A Review on Transdermal Spray: Formulation Aspect Mathews Journal of Pharmaceutical Science A Review on Transdermal Spray: Formulation Aspect. Mathews Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 1(March).
- Maryunis, M., Bakri, S., Patellongi, I., Aman, M., Tahir, T., & Syam, A. (2016). The Effect of the Extracts of Betel (Piper betel) Leaves on the Content of IL-1β as the Inflammatory Cytokine in Experimental Mice Using an Acute Wound Healing Modeling. International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR), 30(1), 180–190. Retrieved from http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=JournalOfBasicAndApplied
- Narayan Singh, S., Singh, G., Mukharjee, A., & Kumar, N. (2021). Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Property & Medicinal Uses of Piper Betle L: a Review. Journal of Natural Remedies, 21(11 (1)).
- Nasruddin, et al, Nakajima, Y., Mukai, K., Setyowati, H., Rahayu, E., & Nur, M. (2014). Cold plasma on full-thickness cutaneous wound accelerates healing through promoting inflammation, re-epithelialization and wound contraction. Clinical Plasma Medicine, 2, 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpme.2014.01.001
- Nasruddin, N., Setyowati, H., Rahayu, E., Wahyuningtyas, E. S., Sikumbang, I. M., Nurani, L. H., Setya, G. (2019). Efektivitas Perlakuan Irisan Daun Lidah Buaya yang Teraktivasi Plasma Jet untuk Mempercepat Penyembuhan Luka Akut Fase Proliferasi. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Unimus, 2, 18–25.
- Nasruddin, Nakajima, Y., Mukai, K., Setyowati, H., Rahayu, E., Sugama, J., & Nakatani, T. (2014). Cold plasma on full-thickness cutaneous wound accelerates healing through promoting inflammation, re-epithelialization and wound contraction. Clinical Plasma Medicine, 2(1), 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpme.2014.01.001
- Nicks, B. A., Ayello, E. A., Woo, K., Nitzki-George, D., & Sibbald, R. G. (2010). Acute wound management: Revisiting the approach to assessment, irrigation, and closure considerations. International Journal of Emergency Medicine, 3(4), 399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12245-010-0217-5
- Nilugal, K. C., Perumal, K., & Ugander, R. E. (2014). Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Piper Betle Leaves and Stem Extract In Experimental Wistar Rats. American Journal of Pharmtech Research, 4(3), 443–452.
- Palumpun, E. F., Wiraguna, A. A. G. P., & Pangkahila, W. (2017). Pemberian ekstrak daun sirih (Piper betle) secara topikal meningkatkan ketebalan epidermis, jumlah fibroblas, dan jumlah kolagen dalam proses penyembuhan luka pada tikus jantan galur Wistar (Rattus norvegicus). Jurnal E-Biomedik, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.35790/ebm.5.1.2017.15037
- Pradhan, D., Suri, K. a, Pradhan, D. K., & Biswasroy, P. (2013). Golden Heart of the Nature: Piper betle L . Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 1(6), 147–167.
- Rahayu, H. S. E., Nasruddin, N., Nurani, L. H., Darmawati, S., Rohmani, A., Lutfiyati, H., Nakatani, T. (2019). Ethanolic extract of the natural product of Daun sirih (Piper betle) leaves may impede the effectiveness of the plasma jet contact style for acute wounds. Clinical Plasma Medicine, 15(18). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpme.2019.100090
- Setyowati, H., Rahayu, E., Nasruddin, N., Hayu, L., & Darmawati, S. (2019). Ethanolic extract of the natural product of Daun sirih (Piper betle) leaves may impede the e ffectiveness of the plasma jet contact style for acute wounds. Clinical Plasma Medicine, 15(18). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpme.2019.100090
- Sikumbang, I. M., Astuti, R. A., Wahyuningtyas, E. S., Lutfiyati, H., Wijayatri, R., & Nasruddin, N. (2020). Wound healing activity of aloe vera extract spray on acute wound in male balb/c mice. Pharmaciana, 10(3), 315. https://doi.org/10.12928/pharmaciana.v10i3.16640
- Tottoli, E. M., Dorati, R., Genta, I., Chiesa, E., Pisani, S., & Conti, B. (2020). Skin wound healing process and new emerging technologies for skin wound care and regeneration. Pharmaceutics, 12(8), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080735
- Umar, R. (2018). Chemical Composition and The Potential Biological Activities of Piper Betel – A. Malaysian Journal of Applied Sciences, 3(1), 1–8.
- Wang, P. H., Huang, B. S., Horng, H. C., Yeh, C. C., & Chen, Y. J. (2018). Wound healing. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, 81(2), 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2017.11.002
- Zar’ah, N. A., Syachruddin, S., & Kusmiyati, K. (2021). The Effect of Green Betel Leaves (Piper betle L.) Extract on Wounding Healing in Mice (Mus musculus L.). Jurnal Biologi Tropis, 21(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.29303/jbt.v21i1.2282
- Zuhdan Fanani, M., & Nugroho, T. (2014). Pengaruh Salep Ekstrak Etanol Daun Sirih (Piper Betle) Terhadap Penyembuhan Luka Iris Pada Tikus Putih Jantan (Rattus norvegicus). Jurnal Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan Indonesia, 6(1), 20–27. https://doi.org/10.20885/jkki.vol6.iss1.art4