Combustion characteristics of pyrolysis oil droplets from pyrolysis of polyethylene (PE) plastic waste
Main Article Content
Abstract
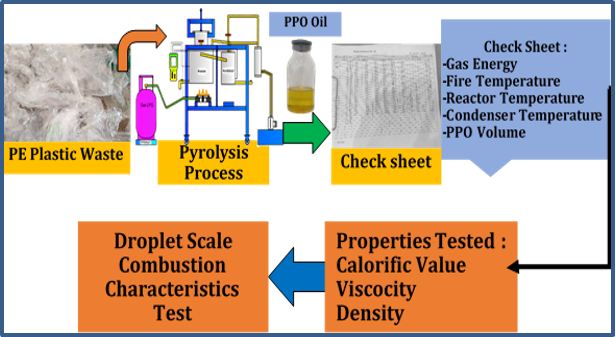
Plastic waste is suspected to be a major contributor to environmental pollution, thus encouraging the need for innovative and effective management strategies to overcome it. Pyrolysis is considered an affordable way to process plastic waste, and even produce useful products in liquid form, which has the potential to be an alternative fuel in combustion engines. This study evaluated the combustion characteristics of pyrolysis oil derived from polyethylene (PE) plastic waste. The pyrolysis process was carried out under controlled conditions, at a furnace temperature of 250°C, a reactor temperature of 400°C, and a condenser temperature of 300°C, processing 1 kg of PE plastic waste. Temperature data was monitored every 10 minutes by installing several thermocouples. The pyrolysis process was able to produce 671 ml of liquid, which was later identified as plastic pyrolysis oil (PPO PE-11) and the rest in the form of residue reached 45 g. The results indicated that PPO PE-11 has a viscosity of 5.93 mm²/s, which is higher than diesel 3.8173 mm²/s. Meanwhile, its density is 0.779 kg/m³, which is slightly lower than diesel. The calorific value of PPO PE-11 is slightly higher than diesel, reaching 11,046.4 cal/g. The droplet scale combustion tests give a shorter ignition delay of 0.6 seconds at 41.28°C for PPO PE-11, compared to 1 second at 52.525°C for diesel, indicating its flammability.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.