Heat transfer performance of Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 ternary nanofluids in plain tube with wire coil inserts
Main Article Content
Abstract
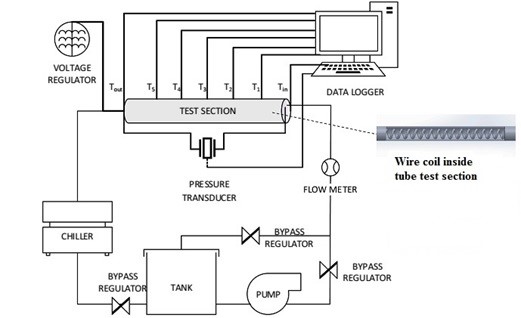
The ternary nanofluids are considered due to their advantages in overcoming the stability drawback of mono and binary nanofluids. This study aims to heat transfer performance of Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 ternary nanofluids in plain tube with wire coil under experimental. The ternary nanofluids were formulated using the composition ratio of 20:16:64 by volume in various volume concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 3.0%. Thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of ternary nanofluids were measured with KD2 Pro Thermal Properties Analyzer and Brookfield LVDV III Rheometer. Experimental forced convection heat transfer was carried out using a fabricated setup for Reynolds numbers from 2,300 to 12,000 at bulk temperature of 70 °C in plain tubes with wire coil inserts (0.83 ≤ P/D ≤ 2.50). Experimental results are highest thermal conductivity enhancement of 24.8% was obtained for ternary nanofluids at 3.0% volume concentration. The 3.0% volume concentration also shows the highest viscosity at all temperatures. The maximum heat transfer improvement for ternary nanofluids in a plain tube with wire coil (P/D-0.83), was attained by 3.0% volume concentration of up to 199.23%. The average TPF of the wire coil increases compared to the plain tube and improves further with volume concentrations in the range of 2.39 to 2.84.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
[2] A. Z. Ziva, Y. K. Suryana, Y. S. Kurniadianti, A. Bayu, D. Nandiyanto, and T. Kurniawan, “Recent Progress on the Production of Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Nanoparticles: A Review,” Mechanical Engineering for Society and Industry, pp. 54–77, 2021, doi: 10.31603/mesi.5493.
[3] S. Pambudi, N. Ilminnafik, S. Junus, and M. N. Kustanto, “Experimental Study on the Effect of Nano Additives γAl2O3 and Equivalence Ratio to Bunsen Flame Characteristic of Biodiesel from Nyamplung (Calophyllum Inophyllum),” Automotive Experiences, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 51–61, 2021, doi: 10.31603/ae.4569.
[4] P. Puspitasari, A. A. Permanasari, A. Warestu, G. P. P. Arifiansyah, D. D. Pramono, and T. Pasang, “Tribology Properties on 5W-30 Synthetic Oil with Surfactant and Nanomaterial Oxide Addition,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 669–686, 2023, doi: 10.31603/ae.10115.
[5] S. Safril, W. H. Azmi, N. N. M. Zawawi, and A. I. Ramadhan, “Tribology Performance of TiO2-SiO2/PVE Nanolubricant at Various Binary Ratios for the Automotive Air-conditioning System,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 485–496, 2023, doi: 10.31603/ae.10255.
[6] S. N. S. Z. Abidin, W. H. Azmi, N. N. M. Zawawi, and A. I. Ramadhan, “Comprehensive Review of Nanoparticles Dispersion Technology for Automotive Surfaces,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 304–327, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.31603/ae.6882.
[7] N. N. M. Zawawi, W. H. Azmi, M. F. Ghazali, and A. I. Ramadhan, “Performance Optimization of Automotive Air-Conditioning System Operating with Al2O3-SiO2/PAG Composite Nanolubricants using Taguchi Method,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 121–136, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.31603/ae.6215.
[8] A. I. Ramadhan, W. H. Azmi, R. Mamat, E. Diniardi, and T. Y. Hendrawati, “Experimental Investigation of Cooling Performance in Automotive Radiator using Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 Nanofluids,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 28–39, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.31603/ae.6111.
[9] A. Kolakoti, M. Setiyo, D. Novia, A. Husaeni, and A. B. Dani, “Enhancing heat transfer performance of automotive car radiator using camphor nanoparticles : experimental study with bibliometric analysis,” Teknomekanik, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 47–67, 2023, doi: 10.24036/teknomekanik.v6i2.25072.
[10] M. Bahrami, M. Akbari, A. Karimipour, and M. Afrand, “An experimental study on rheological behavior of hybrid nanofluids made of iron and copper oxide in a binary mixture of water and ethylene glycol: Non-Newtonian behavior,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 79, pp. 231–237, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.07.015.
[11] A. Boroomandpour, D. Toghraie, and M. Hashemian, “A comprehensive experimental investigation of thermal conductivity of a ternary hybrid nanofluid containing MWCNTs- titania-zinc oxide/water-ethylene glycol (80:20) as well as binary and mono nanofluids,” Synthetic Metals, vol. 268, p. 116501, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116501.
[12] J.-Y. Jung, C. Cho, W. H. Lee, and Y. T. Kang, “Thermal conductivity measurement and characterization of binary nanofluids,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 54, no. 9–10, pp. 1728–1733, Apr. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.01.021.
[13] J. K. Lee, J. Koo, H. Hong, and Y. T. Kang, “The effects of nanoparticles on absorption heat and mass transfer performance in NH3/H2O binary nanofluids,” International Journal of Refrigeration, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 269–275, Mar. 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2009.10.004.
[14] J. Zeng and Y. Xuan, “Enhanced solar thermal conversion and thermal conduction of MWCNT-SiO2/Ag binary nanofluids,” Applied Energy, vol. 212, pp. 809–819, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.12.083.
[15] A. I. Ramadhan, W. H. Azmi, R. Mamat, K. A. Hamid, and S. Norsakinah, “Investigation on stability of tri -hybrid nanofluids in water-ethylene glycol mixture,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 469, p. 012068, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/469/1/012068.
[16] J. Sarkar, P. Ghosh, and A. Adil, “A review on hybrid nanofluids: Recent research, development and applications,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 43, pp. 164–177, Mar. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.023.
[17] S. Guo, S. Dong, and E. Wang, “Gold/Platinum Hybrid Nanoparticles Supported on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Silica Coaxial Nanocables: Preparation and Application as Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, vol. 112, no. 7, pp. 2389–2393, Feb. 2008, doi: 10.1021/jp0772629.
[18] W. H. Azmi, K. Abdul Hamid, A. I. Ramadhan, and A. I. M. Shaiful, “Thermal hydraulic performance for hybrid composition ratio of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids in a tube with wire coil inserts,” Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, vol. 25, p. 100899, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2021.100899.
[19] K. Goudarzi and H. Jamali, “Heat transfer enhancement of Al2O3-EG nanofluid in a car radiator with wire coil inserts,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 118, pp. 510–517, May 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.03.016.
[20] F. Akbaridoust, M. Rakhsha, A. Abbassi, and M. Saffar-Avval, “Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluid heat transfer in helically coiled tubes at constant wall temperature using dispersion model,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 58, no. 1–2, pp. 480–491, Mar. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.11.064.
[21] A. I. Ramadhan, W. H. Azmi, R. Mamat, and K. A. Hamid, “Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and friction factor of plain tube with hybrid nanofluids,” Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, vol. 22, p. 100782, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2020.100782.
[22] S. M. Mousavi, F. Esmaeilzadeh, and X. P. Wang, “Effects of temperature and particles volume concentration on the thermophysical properties and the rheological behavior of CuO/MgO/TiO2 aqueous ternary hybrid nanofluid,” Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, vol. 137, no. 3, pp. 879–901, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1007/s10973-019-08006-0.
[23] H. Adun, D. Kavaz, and M. Dagbasi, “Review of ternary hybrid nanofluid: Synthesis, stability, thermophysical properties, heat transfer applications, and environmental effects,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 328, p. 129525, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129525.
[24] S. Kashyap, J. Sarkar, and A. Kumar, “Performance enhancement of regenerative evaporative cooler by surface alterations and using ternary hybrid nanofluids,” Energy, vol. 225, p. 120199, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.120199.
[25] H. Adun et al., “Synthesis and Application of Ternary Nanofluid for Photovoltaic-Thermal System: Comparative Analysis of Energy and Exergy Performance with Single and Hybrid Nanofluids,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 15, p. 4434, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.3390/en14154434.
[26] A. Dezfulizadeh, A. Aghaei, A. Hassani Joshaghani, and M. M. Najafizadeh, “Exergy efficiency of a novel heat exchanger under MHD effects filled with water-based Cu–SiO2-MWCNT ternary hybrid nanofluid based on empirical data,” Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, vol. 147, no. 7, pp. 4781–4804, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s10973-021-10867-3.
[27] V. Kumar and R. R. Sahoo, “4 E’s (Energy, Exergy, Economic, Environmental) performance analysis of air heat exchanger equipped with various twisted turbulator inserts utilizing ternary hybrid nanofluids,” Alexandria Engineering Journal, vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 5033–5050, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.09.037.
[28] R. R. Sahoo, “Heat transfer and second law characteristics of radiator with dissimilar shape nanoparticle-based ternary hybrid nanofluid,” Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, vol. 146, no. 2, pp. 827–839, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s10973-020-10039-9.
[29] L. Kundan and M. B. Darshan, “Performance investigation of a concentric double tube heat exchanger using twisted tape inserts and nanofluid,” Particulate Science and Technology, pp. 1–18, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1080/02726351.2021.1946729.
[30] N. A. S. Muzaidi et al., “Heat absorption properties of CuO/TiO2/SiO2 trihybrid nanofluids and its potential future direction towards solar thermal applications,” Arabian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 14, no. 4, p. 103059, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103059.
[31] A. N. Abdalla and A. Shahsavar, “An experimental comparative assessment of the energy and exergy efficacy of a ternary nanofluid-based photovoltaic/thermal system equipped with a sheet-and-serpentine tube collector,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 395, p. 136460, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136460.
[32] A. Dezfulizadeh, A. Aghaei, A. H. Joshaghani, and M. M. Najafizadeh, “An experimental study on dynamic viscosity and thermal conductivity of water-Cu-SiO2-MWCNT ternary hybrid nanofluid and the development of practical correlations,” Powder Technology, vol. 389, pp. 215–234, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.05.029.
[33] R. R. Sahoo and V. Kumar, “Development of a new correlation to determine the viscosity of ternary hybrid nanofluid,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 111, p. 104451, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.104451.
[34] N. A. Shah, A. Wakif, E. R. El-Zahar, T. Thumma, and S.-J. Yook, “Heat transfers thermodynamic activity of a second-grade ternary nanofluid flow over a vertical plate with Atangana-Baleanu time-fractional integral,” Alexandria Engineering Journal, vol. 61, no. 12, pp. 10045–10053, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2022.03.048.
[35] H. R. Allahyar, F. Hormozi, and B. ZareNezhad, “Experimental investigation on the thermal performance of a coiled heat exchanger using a new hybrid nanofluid,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 76, pp. 324–329, Sep. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.03.027.
[36] M. Afrand, D. Toghraie, and B. Ruhani, “Effects of temperature and nanoparticles concentration on rheological behavior of Fe 3 O 4 –Ag/EG hybrid nanofluid: An experimental study,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 77, pp. 38–44, Oct. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.04.007.
[37] M. Hemmat Esfe et al., “Thermal conductivity of Cu/TiO2–water/EG hybrid nanofluid: Experimental data and modeling using artificial neural network and correlation,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 66, pp. 100–104, Aug. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.05.014.
[38] K. A. Hamid, W. H. Azmi, M. F. Nabil, and R. Mamat, “Improved thermal conductivity of TiO 2 –SiO 2 hybrid nanofluid in ethylene glycol and water mixture,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 257, p. 012067, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/257/1/012067.
[39] G. Huminic and A. Huminic, “The heat transfer performances and entropy generation analysis of hybrid nanofluids in a flattened tube,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 119, pp. 813–827, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.155.
[40] M. S. Ahmed and A. M. Elsaid, “Effect of hybrid and single nanofluids on the performance characteristics of chilled water air conditioning system,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 163, p. 114398, Dec. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114398.
[41] L. S. Sundar, M. K. Singh, and A. C. M. Sousa, “Enhanced heat transfer and friction factor of MWCNT–Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluids,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 52, pp. 73–83, Mar. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2014.01.012.
[42] T. T. Baby and S. Ramaprabhu, “Experimental investigation of the thermal transport properties of a carbon nanohybrid dispersed nanofluid,” Nanoscale, vol. 3, no. 5, p. 2208, 2011, doi: 10.1039/c0nr01024c.
[43] O. Keklikcioglu and V. Ozceyhan, “Experimental investigation on heat transfer enhancement in a circular tube with equilateral triangle cross sectioned coiled-wire inserts,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 131, pp. 686–695, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.12.051.
[44] P. Promvonge, “Thermal augmentation in circular tube with twisted tape and wire coil turbulators,” Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 2949–2955, Nov. 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2008.06.022.
[45] M. A. Akhavan-Behabadi, M. Shahidi, and M. R. Aligoodarz, “An experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of MWCNT–water nano-fluid inside horizontal coiled wire inserted tube,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 63, pp. 62–72, Apr. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.02.013.
[46] A. García, J. P. Solano, P. G. Vicente, and A. Viedma, “Enhancement of laminar and transitional flow heat transfer in tubes by means of wire coil inserts,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 50, no. 15–16, pp. 3176–3189, Jul. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.01.015.
[47] K. Abdul Hamid, W. H. Azmi, R. Mamat, and K. V. Sharma, “Heat transfer performance of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids in a tube with wire coil inserts,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 152, pp. 275–286, Apr. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.02.083.
[48] P. Promvonge, N. Koolnapadol, M. Pimsarn, and C. Thianpong, “Thermal performance enhancement in a heat exchanger tube fitted with inclined vortex rings,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 285–292, Jan. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.09.031.
[49] S. K. Saha, “Thermal and friction characteristics of laminar flow through rectangular and square ducts with transverse ribs and wire coil inserts,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 63–72, Jan. 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2009.09.003.
[50] Z. Feng, X. Luo, F. Guo, H. Li, and J. Zhang, “Numerical investigation on laminar flow and heat transfer in rectangular microchannel heat sink with wire coil inserts,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 116, pp. 597–609, Apr. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.091.
[51] S. S. Chougule, V. V. Nirgude, P. D. Gharge, M. Mayank, and S. K. Sahu, “Heat Transfer Enhancements of Low Volume Concentration CNT/Water Nanofluid and Wire Coil Inserts in a Circular Tube,” Energy Procedia, vol. 90, pp. 552–558, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2016.11.223.
[52] J. P. Solano, R. Herrero, S. Espín, A. N. Phan, and A. P. Harvey, “Numerical study of the flow pattern and heat transfer enhancement in oscillatory baffled reactors with helical coil inserts,” Chemical Engineering Research and Design, vol. 90, no. 6, pp. 732–742, Jun. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2012.03.017.
[53] A. García, J. P. Solano, P. G. Vicente, and A. Viedma, “Flow pattern assessment in tubes with wire coil inserts in laminar and transition regimes,” International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 516–525, Jun. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2006.07.001.
[54] S. Rana, H. Zahid, R. Kumar, R. S. Bharj, P. K. S. Rathore, and H. M. Ali, “Lithium-ion battery thermal management system using MWCNT-based nanofluid flowing through parallel distributed channels: An experimental investigation,” Journal of Energy Storage, vol. 81, p. 110372, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.110372.
[55] C. Liu et al., “Recent advances of plasmonic nanofluids in solar harvesting and energy storage,” Journal of Energy Storage, vol. 72, p. 108329, Nov. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.108329.
[56] Yew Wai Loon and Nor Azwadi Che Sidik, “A comprehensive review of recent progress of nanofluid in engineering application: Microchannel heat sink (MCHS),” Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 1–25, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.37934/araset.28.2.125.
[57] W. H. Azmi, K. Abdul Hamid, N. A. Usri, R. Mamat, and M. S. Mohamad, “Heat transfer and friction factor of water and ethylene glycol mixture based TiO 2 and Al 2 O 3 nanofluids under turbulent flow,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 76, pp. 24–32, Aug. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.05.010.
[58] M. F. Nabil, W. H. Azmi, K. A. Hamid, and R. Mamat, “Heat transfer and friction factor of composite TiO 2 –SiO 2 nanofluids in water-ethylene glycol (60:40) mixture,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 257, p. 012066, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/257/1/012066.
[59] National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), “Ethylene Glycol: Systemic Agent,” CDC, 2021. .
[60] W. H. Azmi, “Heat transfer augmentation of water based TiO2 and SiO2 nanofluids in a tube with twisted tape,” Universiti Malaysia Pahang, 2015.
[61] M. T. Naik, S. S. Fahad, L. Syam Sundar, and M. K. Singh, “Comparative study on thermal performance of twisted tape and wire coil inserts in turbulent flow using CuO/water nanofluid,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 57, pp. 65–76, Sep. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.04.006.
[62] Y. Cengel and A. Ghajar, Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals and Applications, 4th in SI. New York: Mc Graw Hill, 2011.
[63] H. Blasius, “Das Aehnlichkeitsgesetz bei Reibungsvorgängen in Flüssigkeiten,” in Mitteilungen über Forschungsarbeiten auf dem Gebiete des Ingenieurwesens, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1913, pp. 1–41.
[64] J.-Y. San, W.-C. Huang, and C.-A. Chen, “Experimental investigation on heat transfer and fluid friction correlations for circular tubes with coiled-wire inserts,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 65, pp. 8–14, Jul. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.04.008.
[65] L. S. Sundar, M. K. Singh, V. Punnaiah, and A. C. M. Sousa, “Experimental investigation of Al2O3/water nanofluids on the effectiveness of solar flat-plate collectors with and without twisted tape inserts,” Renewable Energy, vol. 119, pp. 820–833, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.10.056.
[66] M. Saeedinia, M. A. Akhavan-Behabadi, and M. Nasr, “Experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of nanofluid flow in a horizontal coiled wire inserted tube under constant heat flux,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 36, pp. 158–168, Jan. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2011.09.009.
[67] T. Srinivas and A. Venu Vinod, “Heat transfer intensification in a shell and helical coil heat exchanger using water-based nanofluids,” Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, vol. 102, pp. 1–8, Apr. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2016.01.005.
[68] S. Eiamsa-ard and K. Kiatkittipong, “Heat transfer enhancement by multiple twisted tape inserts and TiO2/water nanofluid,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 896–924, Sep. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.05.062.
[69] P. K. Sarma, T. Subramanyam, P. S. Kishore, V. D. Rao, and S. Kakac, “Laminar convective heat transfer with twisted tape inserts in a tube,” International Journal of Thermal Sciences, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 821–828, Sep. 2003, doi: 10.1016/S1290-0729(03)00055-3.
[70] M. Chandrasekar, S. Suresh, and A. Chandra Bose, “Experimental studies on heat transfer and friction factor characteristics of Al2O3/water nanofluid in a circular pipe under laminar flow with wire coil inserts,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 122–130, Feb. 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2009.10.001.
[71] K. A. Hamid, W. H. Azmi, M. F. Nabil, R. Mamat, and K. V. Sharma, “Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity on nanoparticle mixture ratios of TiO2-SiO2 nanofluids,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 116, pp. 1143–1152, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.09.087.
[72] M. Asadi and A. Asadi, “Dynamic viscosity of MWCNT/ZnO–engine oil hybrid nanofluid: An experimental investigation and new correlation in different temperatures and solid concentrations,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 76, pp. 41–45, Aug. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.05.019.
[73] F. W. Dittus and L. M. K. Boelter, “Heat transfer in automobile radiators of the tubular type,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 3–22, Jan. 1985, doi: 10.1016/0735-1933(85)90003-X.
[74] D. K. Agarwal, A. Vaidyanathan, and S. Sunil Kumar, “Investigation on convective heat transfer behaviour of kerosene-Al 2 O 3 nanofluid,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 84, pp. 64–73, Jun. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.03.054.
[75] K. Sharifi, M. Sabeti, M. Rafiei, A. H. Mohammadi, and L. Shirazi, “Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) technique to study the effects of helical wire inserts on heat transfer and pressure drop in a double pipe heat exchanger,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 128, pp. 898–910, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.08.146.