Main Article Content
Abstract
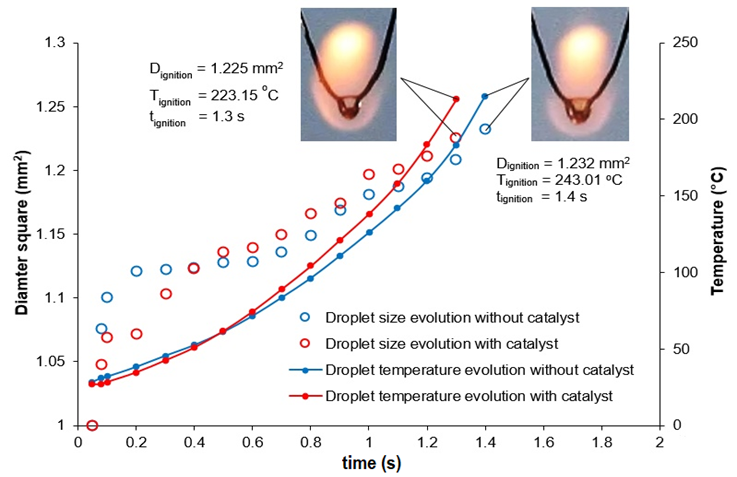
The tests revealed the exceptional combustion properties of a blended fuel consisting of castor oil and rhodium liquid (Rhl) as a highly effective homogeneous combustion catalyst. Our findings indicate that castor oil's unique molecular structure makes it an ideal fuel component, and the catalyst interacts with the fuel's triglycerides to enhance fuel properties and facilitate ignition.These findings support the pivotal role of the synthetic catalyst Rhl, which effectively reduces the binding forces within the triglyceride chain through polarization interactions. As a result, molecular bonds become more flexible, providing electrons with greater freedom of movement. Synthetic catalysts induce significant modifications in the triglyceride structure, increasing electron energy levels and enhancing the reactivity of fuel molecules, ultimately leading to improved fuel combustion efficiency. Integrating the Rhl synthetic catalyst also enhances fuel performance by reducing ignition duration and increasing the combustion rate. The elevated combustion temperatures of the fuel droplets highlight the effectiveness of promoting environmentally sustainable combustion processes.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
- S. Piazzi, S. S. Ail, V. Benedetti, F. Patuzzi, and M. Baratieri, “Fuel-lean combustion synthesized cobalt catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch reaction,” Catalysis Today, no. April, pp. 0–1, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.06.088.
- D. P. Matharasi, G. Ramya, A. Asha, and P. Jayaprakash, “A study on the production and engine analysis of organic liquid fuel from jatropha and castor oil by catalytic cracking over solid acid catalysts,” Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, vol. 99, no. 11, p. 100757, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jics.2022.100757.
- C. Özyalcin, S. Sterlepper, S. Roiser, H. Eichlseder, and S. Pischinger, “Exhaust gas aftertreatment to minimize NOX emissions from hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines,” Applied Energy, vol. 353, p. 122045, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122045.
- B. Ashok et al., “Multi-functional fuel additive as a combustion catalyst for diesel and biodiesel in CI engine characteristics,” Fuel, vol. 278, no. May, p. 118250, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118250.
- P. S. Yadav, Z. Said, R. Gautam, R. Raman, and H. Caliskan, “Novel investigation on atomization, performance, and emission characteristics of preheated jatropha oil methyl ester and ethyl ester,” Energy, vol. 270, p. 126870, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.126870.
- N. Talib, N. F. A. M. Sukor, A. M. Sabri, H. Abdullah, and A. S. A. Sani, “Experimental study on physical properties of modified jatropha oil-based nanofluids for machining purposes,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 48, pp. 1831–1835, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.141.
- M. Sui, Z. Zhu, F. Li, and H. Wang, “Effect of ferrocene as a combustion catalyst on the premixed combustion flame characteristics of Jatropha biodiesel,” Combustion and Flame, vol. 259, p. 113180, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2023.113180.
- A. Ashok, S. K. Gugulothu, R. V. Reddy, and B. Burra, “Influence of 1-pentanol as the renewable fuel blended with jatropha oil on the reactivity controlled compression ignition engine characteristics and trade-off study with variable fuel injection pressure,” Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 52, p. 102215, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2022.102215.
- H. Sachdeva, “Recent advances in the catalytic applications of GO/rGO for green organic synthesis,” Green Processing and Synthesis, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 515–537, 2020, doi: 10.1515/gps-2020-0055.
- M. M. Khan, A. Kumar Kadian, and R. P. Sharma, “Investigation of high fuel injection pressure variation on compression ignition engines powered by jatropha oil methyl ester-heptanol-diesel blends,” Alexandria Engineering Journal, vol. 65, pp. 675–688, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2022.10.009.
- G. S. Kim, B. Y. Lee, G. Accardo, H. C. Ham, J. Moon, and S. P. Yoon, “Improved catalytic activity under internal reforming solid oxide fuel cell over new rhodium-doped perovskite catalyst,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 423, pp. 305–315, May 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.03.082.
- N. Pal et al., “Hydrotreating and hydrodemetalation of raw jatropha oil using mesoporous Ni-Mo/γ-Al2O3 catalyst,” Fuel, vol. 326, p. 125108, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125108.
- H. Tang et al., “Production of jet fuel range hydrocarbons using a magnetic Ni–Fe/SAPO-11 catalyst for solvent-free hydrodeoxygenation of jatropha oil,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 177, p. 106927, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2023.106927.
- G. Brinklow et al., “Impact of Cylinder Deactivation Strategies on Three-way Catalyst Performance in High Efficiency Low Emissions Engines,” Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, vol. 14, p. 100481, May 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.ceja.2023.100481.
- R. Sui, J. Mantzaras, and R. Bombach, “H2 and CO heterogeneous kinetic coupling during combustion of H2/CO/O2/N2 mixtures over rhodium,” Combustion and Flame, vol. 202, pp. 292–302, Apr. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.01.021.
- R. N. E. Tiri et al., “Improving hydrogen generation from dehydrogenation of dimethylamine borane using polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilized platinum-rhodium nanoclusters as highly efficient and reusable catalysts: Development of ANN model,” Chemical Engineering Research and Design, vol. 182, pp. 305–311, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2022.04.005.
- A. Al Assadi et al., “Challenges and prospects of automated disassembly of fuel cells for a circular economy,” Resources, Conservation & Recycling Advances, vol. 19, p. 200172, Nov. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.rcradv.2023.200172.
- M. S. Leguizamón Aparicio, M. A. Ocsachoque, E. Rodríguez-Castellón, D. Gazzoli, M. L. Casella, and I. D. Lick, “Promoting effect of rhodium on Co/ZnAl2O4 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of hydrocarbons,” Catalysis Today, vol. 372, no. July, pp. 2–10, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.10.006.
- S. Neuberg, H. Pennemann, V. Shanmugam, R. Zapf, and G. Kolb, “Promoting effect of Rh on the activity and stability of Pt-based methane combustion catalyst in microreactors,” Catalysis Communications, vol. 149, p. 106202, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2020.106202.
- H. Y. Nanlohy, I. N. G. Wardana, N. Hamidi, L. Yuliati, and T. Ueda, “The effect of Rh3+ catalyst on the combustion characteristics of crude vegetable oil droplets,” Fuel, vol. 220, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.001.
- H. Y. Setyawan, M. Zhu, Z. Zhang, and D. Zhang, “Ignition and combustion characteristics of single droplets of a crude glycerol in comparison with pure glycerol, petroleum diesel, biodiesel and ethanol,” Energy, vol. 113, pp. 153–159, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.07.032.
- D. Xun, X. Sun, Z. Liu, F. Zhao, and H. Hao, “Comparing supply chains of platinum group metal catalysts in internal combustion engine and fuel cell vehicles: A supply risk perspective,” Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, vol. 4, p. 100043, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.clscn.2022.100043.
- S. Özkar, “Increasing the catalytic efficiency of rhodium(0) nanoparticles in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol. 54, pp. 327–343, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.03.322.
- J. Mantzaras, R. Sui, and R. Bombach, “Fuel-rich hetero-/homogeneous combustion of C3H8/O2/N2 mixtures over rhodium,” Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 5601–5610, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2022.06.009.
- E. Zambrzycka-Szelewa and B. Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, “Fast and simple method for simultaneous determination of palladium and rhodium in spent automotive catalysts by high-resolution continuum source electrothermal atomic absorption spectroscopy,” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, vol. 213, p. 106859, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2024.106859.
- H. Y. Nanlohy, I. N. G. Wardana, M. Yamaguchi, and T. Ueda, “The role of rhodium sulfate on the bond angles of triglyceride molecules and their effect on the combustion characteristics of crude jatropha oil droplets,” Fuel, vol. 279, p. 118373, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118373.
- I. N. G. Wardana, “Combustion characteristics of jatropha oil droplet at various oil temperatures,” Fuel, vol. 89, no. 3, pp. 659–664, 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.07.002.
- H. Riupassa et al., “Effects of Eugenol and Cineol Compound on Diffusion Burning Rate Characteristics of Crude Coconut Oil Droplet,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 59–67, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.31603/ae.8150.
- A. Hoxie, R. Schoo, and J. Braden, “Microexplosive combustion behavior of blended soybean oil and butanol droplets,” Fuel, vol. 120, pp. 22–29, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.11.036.
- H. Riupassa, S. Suyatno, and H. Y. Nanlohy, “Identifying the Effect of Aromatic Compounds on the Combustion Characteristics of Crude Coconut Oil Droplet,” Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, vol. 2, no. 6–122, pp. 6–14, 2023, doi: 10.15587/1729-4061.2023.272289.
- H. Y. Nanlohy, “Comparative Studies on Combustion Characteristics of Blended Crude Jatropha Oil with Magnetic Liquid Catalyst and DEX under Normal Gravity Condition,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science and Technology, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 79–88, 2021, doi: 10.17977/um016v5i22021p079.
- H. Y. Nanlohy and H. Riupassa, “An Experimental Study on the Ignition Behavior of Blended Fuels Droplets with Crude Coconut Oil and Liquid Metal Catalyst,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 39–45, 2020, doi: 10.31603/ae.v3i2.3481.
- Suyatno, H. Riupassa, S. Marianingsih, and H. Y. Nanlohy, “Characteristics of SI engine fueled with BE50-Isooctane blends with different ignition timings,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 1, p. e12922, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12922.
- H. Y. Nanlohy, H. Riupassa, and M. Setiyo, “Characterizing of Nano Activated Bio-Carbon of Sago Waste as a Homogeneous Combustion Catalyst,” Automotive Experiences, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 77–85, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.31603/ae.10619.