Main Article Content
Abstract
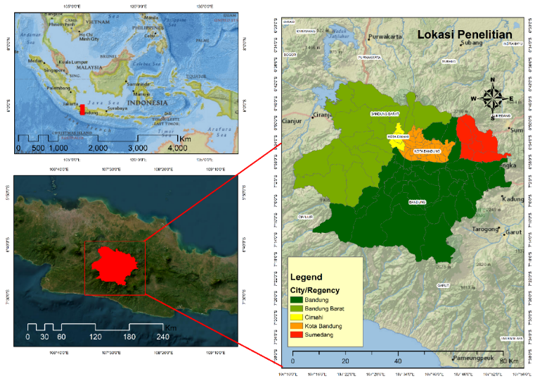
The current mapping challenge is to obtain land cover information with a very high level of accuracy. This information can be useful for regional development, especially in the Bandung Basin Urban Area (KPCB). One of the problems in KPCB is spatial planning issues regarding land cover development. One approach to obtaining land cover information is by utilizing remote sensing technology using the Support Vector Machine (SVM) method. The research method employed in this study is remote sensing, with a unit of analysis based on Regency/City administrative boundaries. The data used in this research consists of Landsat imagery recorded in 2023. The aim of this research is to classify land cover and assess accuracy using the SVM method in KPCB. The SVM results provide information on six land covers: water bodies, secondary forests and mixed gardens, wet agricultural land, dry agricultural land, plantations, built-up land, and primary forests. The accuracy test yielded an overall accuracy of 90% and a kappa value of 0.88. The obtained accuracy in land cover classification is very high, indicating that the data used can be employed for further analysis. For instance, spatial analysis reveals that built-up land development in KPCB tends towards the south, highlighting the phenomenon of urban sprawl. Thus, the utilization of remote sensing technology for land cover information can offer valuable policy insights for addressing spatial planning and development in KPCB.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
- Badan Pengelola Cekungan Bandung, “Laporan Tahunan Badan Pengelola Kawasan Perkotaan Cekungan Bandung-Tahun 2021,” Bandung, Laporan, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://cekunganbandung.jabarprov.go.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Laporan-Tahunan-BP-Cekban-2021.pdf
- Presiden Republik Indonesia, “Peraturan Preseiden Republik Indonesia Nomor 45 Tahun 2018 Tentang Rencana Tata Ruang Kawasan Perkotaan Cekungan Bandung.” 2018.
- L. N. Fuadina, E. Rustiadi, and A. E. Pravitasari, “Analisis faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi urban sprawl di kawasan cekungan Bandung,” TATALOKA, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 105–114, 2021.
- P. Gong et al., “Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: first mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data,” International Journal of Remote Sensing, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 2607–2654, Apr. 2013, doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.748992.
- I. Kustiwan and A. Ladimananda, “Pemodelan Dinamika Perkembangan Perkotaan Dan Daya Dukung Lahan Di Kawasan Cekungan Bandung,” TATALOKA, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 98–112, Jan. 2016, doi: 10.14710/tataloka.14.2.98-112.
- P. Danoedoro, “Pengantar penginderaan jauh digital,” Penerbit Andi, Yogyakarta, 2012.
- I. Fardani, F. A. J. Mohmed, and I. Chofyan, “Pemanfaatan prediksi tutupan lahan berbasis cellular automata-markov dalam evaluasi rencana tata ruang,” Media Komunikasi Geografi, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 157–169, 2020.
- A. A. Purboyo, “Analisis Perubahan Kekritisan Lingkungan Menggunakan Algoritma Environmental Criticality Index Di Kota Depok Tahun 2000-2021,” Skripsi, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, 2022. [Online]. Available: http://repository.upi.edu/
- L. Muta’Ali, Teknik analisis regional untuk perencanaan wilayah, tata ruang dan lingkungan, 1st ed. Yogyakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Geografi (BPFG), Universitas Gadjah Mada, 2015.
- W. Utami, A. Rahman, and S. Sutaryono, “Pendekatan Interpretasi Visual Dan Digital Citra Pleiades Untuk Klasifikasi Penutup Lahan,” Geography: Jurnal Kajian, Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 18–31, 2022.
- S. Fitri and N. Nurjanah, “PENERAPAN SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE UNTUK MENDAPATKAN SEBARAN LAHAN SAWAH PADA CITRA LANDSAT 8,” INFOTECH journal, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 51–55, 2018.
- A. N. R. W. Hamdir, “Studi Perbandingan Klasifikasi Multispektral Maximum Likelihood dan Support Vector Machine untuk Pemetaan Penutup Lahan,” Jurnal Bumi Indonesia, vol. 3, no. 4, 2014, Accessed: Dec. 29, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/295176196.pdf
- D. Suyanto, “Data Mining untuk klasifikasi dan klasterisasi data,” Bandung: Informatika Bandung, 2017.
- N. M. Farda, “Multi-temporal land use mapping of coastal wetlands area using machine learning in Google earth engine,” in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, IOP Publishing, 2017, p. 012042. Accessed: Jan. 26, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/98/1/012042/meta
- M. Kamal, I. Jamaluddin, A. Parela, and N. M. Farda, “Comparison of Google Earth Engine (GEE)-based machine learning classifiers for mangrove mapping,” in Proceedings of the 40th Asian Conference Remote Sensing, ACRS, 2019, pp. 1–8.
- M. I. Hariyono, Rokhmatuloh, and R. S. Dewi, “LAND USE AND LAND COVER (LULC) CLASSIFICATION WITH MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH USING ORTHOPHOTO DATA,” Majalah Ilmiah Globe, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 87–89, 2023.
- Sutanto, Metode Penelitian Penginderaan Jauh. in II. Yogyakarta: OMBAK, 2016.
- A. Jamil and B. Bayram, “Tree species extraction and land use/cover classification from high-resolution digital orthophoto maps,” IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 89–94, 2017.
- R. Qin, “A mean shift vector-based shape feature for classification of high spatial resolution remotely sensed imagery,” IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 1974–1985, 2014.
- T. Lillesand, R. W. Kiefer, and J. Chipman, Remote sensing and image interpretation. John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
- I. Jaya, Penginderaan Jauh Satelit Untuk Kehutanan Jurusan Manajemen Hutan. Bogor: Fakultas Kehutanan IPB, 2002.
- D. D. Unaradjan, Metode penelitian kuantitatif. Penerbit Unika Atma Jaya Jakarta, 2019.
- H. S. Yunus, Metodologi Penelitian Wilayah Kontemporer. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Belajar, 2010.
- N. T. Sugito, I. Gumilar, S. Hendriatiningsih, and B. E. Leksono, “Integration of Market Price Comparison Approach and Income Capitalization Approach in Urban Land Valuation,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 1127, no. 1, p. 012036, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1127/1/012036.
- S. Wangsaatmaja, A. Sabar, and M. A. Prasetiati, “Permasalahan dan Strategi Pembangunan Lingkungan Berkelanjutan Studi Kasus: Cekungan Bandung,” Indonesian Journal on Geoscience, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 163–171, 2006.
- L. Nurliana and L. E. Widodo, “Potensi Imbuhan dan Imbuhan Airtanah Cekungan Airtanah Bandung,” JTM, vol. 16, pp. 261–268, 2009.