Main Article Content
Abstract
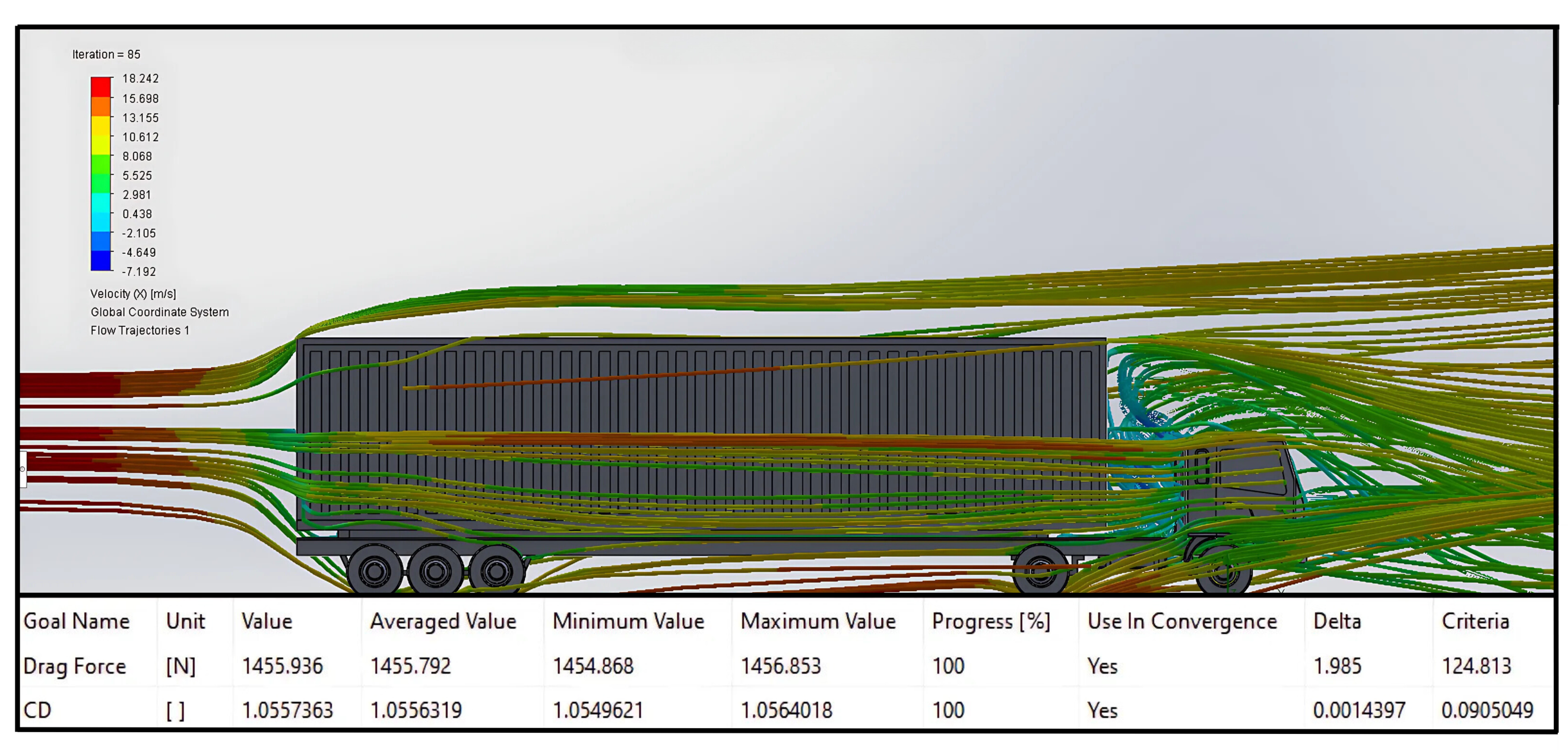
Fuel efficiency in heavy-duty trucks in Indonesia faces significant challenges, while the current HDM-4 fuel consumption model has limitations in reflecting local conditions. This study calibrates the HDM-4 model using telematics data, engine speed modeling, aerodynamic simulations, and calibration factors. The novelty lies in updating parameters such as engine speed, vehicle frontal area, and calibration factors for engine power efficiency (Kpea) and rolling resistance (Kcr2) to account for tire-road interaction in Indonesian conditions. Data were collected from 5-axle trucks on the Tanjung Priok–Bandung toll road, analyzed using regression, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations, and non-parametric paired tests. Results show updated engine speed parameters (RPM_a0 = 680.11, RPM_a1 = -4.9031, RPM_a2 = 0.3858, RPM_a3 = -0.0028), a drag coefficient of 1.0556, and a frontal area of 8.2 m². Calibrating Kpea and Kcr2 (both 0.6) improved prediction accuracy, with no significant difference between predicted and observed data (p = 0.186). The enhanced HDM-4 model supports operational decisions, infrastructure planning, and sustainable transport policies, improving energy efficiency, reducing emissions, and boosting national logistics competitiveness.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.